Informing practice and policy in low-resource settings: Rapid reviews of the diabetic retinopathy evidence
Background
The aim of this project was to identify, critically review and combine the published evidence on interventions that work for the management of DR in LMICs. The outputs of this project are to be disseminated to relevant stakeholders, programme implementers and policy makers, to inform cost-effective and innovative approaches to deliver DR programmes in LMICs.
Four rapid reviews were conducted. The research questions addressed common points at which people with diabetes can drop out of the care journey:
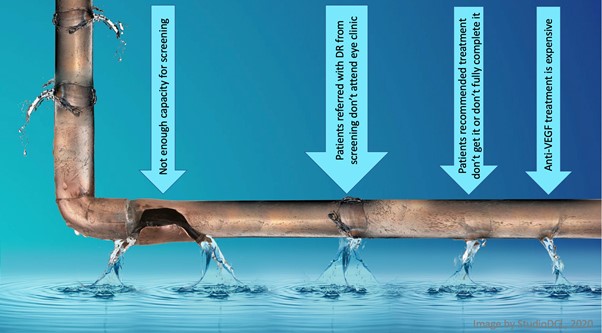
- Can task-shifting improve the detection of diabetic retinopathy (DR) compared with eye examination done by ophthalmologists among adults with diabetes in LMICs
- What interventions are effective in increasing successful referral to eye health services for people with suspected or diagnosed DR or DMO in LMICs?
- What interventions are effective in increasing uptake and completion of treatment for DR and /or DMO among people with diabetes in LMICs?
- Is vial-sharing of anti-VEGF for multiple patients safe in the treatment of PDR and DMO in LMICs compared with using a new vial in each patient?
Acknowledgements and funding
This was a collaborative research project with The Fred Hollows Foundation,Australia.
The project was funded by FHF Australia.
Associated materials
The registered protocols for the four rapid reviews are available on OSF (https://osf.io/dashboard)
- Bascaran, C., Mwangi, N., D’Esposito, F., Mdala, S., Ulloa, J. A. L., Gordon, I., … Burton, M. (2020, November 16). Effectiveness of task-shifting for the detection of diabetic retinopathy in low- and middle-income countries: a rapid review protocol. https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/DFHG6
- Bascaran, C., Mwangi, N., D’Esposito, F., Cleland, C. R., Ulloa, J. A. L., Gordon, I., … Burton, M. (2020, October 2). Effectiveness of interventions to increase uptake and completion of treatment for diabetic retinopathy in low- and middle-income countries: a rapid review protocol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-020-01562-9
- Mwangi, N., Bascaran, C., D’Esposito, F., Gordon, I., Mutie, D., Niyonzima, J.-C., … Burton, M. (2020, May 2). Interventions to promote successful referral to eye services for people with suspected diabetic retinopathy or macula oedema in low- and middle income countries: protocol for a rapid review. Retrieved from osf.io/djzm
- Mwangi, N., Bascaran, C., D’Esposito, F., Gordon, I., Niyonzima, J.-C., Khanal, S., … Burton, M. (2020, May 2). Using one vial of anti-VEGFs for multiple patients with vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy in low- and middle-income countries: protocol for a rapid review. Retrieved from osf.io/9gxz7
Associated publications
One protocol has been accepted for publication on BMC Systematic Reviews; the other three protocols have been submitted for publication and are awaiting editors’ decisions.
The reviews have been written as reports and are under review with the FHF team.
The reviews are being submitted for publication in peer reviewed journals.
Specific contacts
Grant co-PIs:
Nyawira Mwangi, nmwangi09@gmail.com
Cova Bascaran, Covadonga.bascaran@lshtm.ac.uk
